LONDON: Lily Greenberg-Call recently became the latest Biden administration official to step down in protest over the White House’s handling of the war in Gaza, amid a string of resignations from the US Department of State.
Greenberg-Call, who left her position at the Department of the Interior in mid-May, slammed the Biden administration for having “enabled and legitimized” Israel’s onslaught on the Gaza Strip.
In her resignation letter, she said she “can no longer in good conscience continue to represent this administration amidst President Biden’s disastrous, continued support for Israel’s genocide in Gaza.”
Biden’s policy in the Middle East has repeatedly come under fire since the onset of Israel’s military campaign in Gaza, particularly over the supply of weapons to the Israel Defense Forces, which rights groups say have been used to harm civilians.
The Israeli military’s bombing campaign in Gaza in retaliation for the Hamas-led Oct. 7 attack on southern Israel has killed at least 35,000 Palestinians, razed entire neighborhoods, destroyed the enclave’s infrastructure, and displaced 90 percent of the population.
Israel and senior figures in the Biden administration have said Hamas shares in the blame for the high civilian death toll in Gaza.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Jake Sullivan, the US national security adviser, has previously said that Hamas’ tactics have placed “an incredible burden on the IDF, a burden that is unusual for a military in today’s day and age,” by hiding behind civilians as it conducts its war with Israeli forces.
The day Greenberg-Call resigned, the Biden administration told Congress it planned to send $1 billion in new military aid to Israel, despite the president’s opposition to a full-scale invasion of Rafah in southern Gaza, the Associated Press reported. It will be the US’ first arms shipment to Israel since Biden paused the transfer of 3,500 bombs earlier in the month.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced in April that Israeli troops would expand operations into Rafah — Gaza’s southernmost city. On May 6, Israel mounted a limited operation in Rafah, seizing control of its border crossing with Egypt.
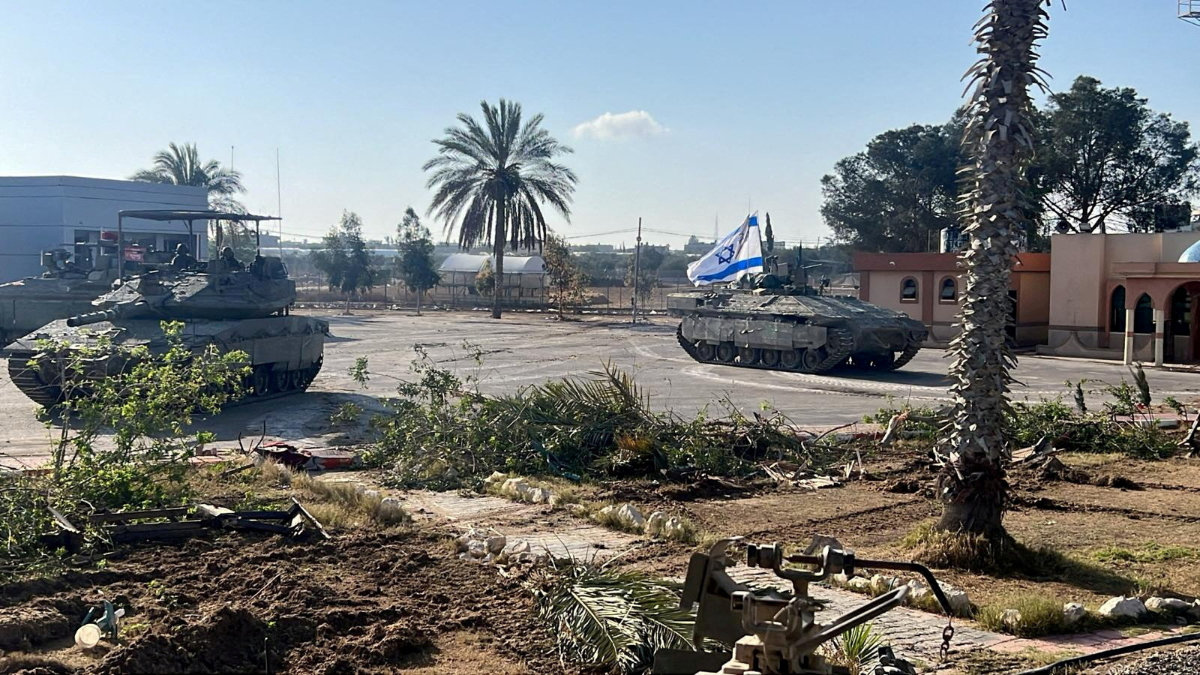

Israeli military vehicles operate in the Gazan side of the Rafah Crossing in the southern Gaza Strip, in this handout image released on May 7, 2024. (Israel Defense Forces/Handout via REUTERS)
The US government said it had halted the bomb shipment to prevent Israel from using the munitions in its attack on Rafah, an area densely populated with civilians, most of whom have been displaced multiple times.
However, a lower chamber bill on May 16 condemned Biden for the suspension and voted to override it, with Republicans saying the president should not dictate how Israel uses American weapons in its war against Hamas.
But the US Arms Export Control Act of 1961 gives the President the authority to halt — or even terminate — American arms transfers if he finds that the recipient country “has used such articles for unauthorized purposes,” according to a 2020 report by the Congressional Research Service.
The vote prompted some 30 Congressional staffers to march to the base of the steps of the House of Representatives at the US Capitol, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and protesting the vote.

Thirty congressional staffers marched on the House of Representatives in Washington D.C. on May 16, 2024, to demand a ceasefire in Gaza. (AFP)
After announcing the halt on the bomb shipment, Biden told CNN that US-manufactured weapons had been used to kill civilians in Gaza.
“Civilians have been killed in Gaza as a consequence of those bombs and other ways in which they go after population centers,” he said on May 8.
“I made it clear that if they go into Rafah — they haven’t gone in Rafah yet — if they go into Rafah, I’m not supplying the weapons that have been used historically to deal with Rafah, to deal with the cities — that deal with that problem.”
According to the Washington Post, the US has made more than 100 weapons sales to Israel since the start of the war in Gaza. The sales reportedly included precision-guided munitions, small-diameter bombs, bunker busters, small arms, and more.
In late April, human-rights monitor Amnesty International submitted a 19-page report to US authorities claiming that US weapons provided to Israel had been “used in serious violations of international humanitarian and human rights law, and in a manner that is inconsistent with US law and policy.”
The newly revised US Conventional Arms Transfer Policy, released in February last year, stipulates “preventing arms transfers that risk facilitating or otherwise contributing to violations of human rights or international humanitarian law.”
Hala Rharrit, who stepped down as the Arabic-language spokesperson of the US Department of State in April after 18 years of service over the Biden administration’s policy on Gaza, stressed that the government should “abide by our own laws.”
She told Arab News: “We have systems in place within the State Department to ensure that our weaponry is not used to kill civilians, with requirements put in place requiring recipient countries to limit harm to civilians — to include both civilian populations and civilian infrastructure.
“There are multiple laws on the books that we are ignoring as a State Department — willfully ignoring,” she continued. “There’s the Arms Export Control Act, there’s the Foreign Assistance Act, the Leahy Law — there are multiple regulations that would ensure what’s happening now would never happen.”
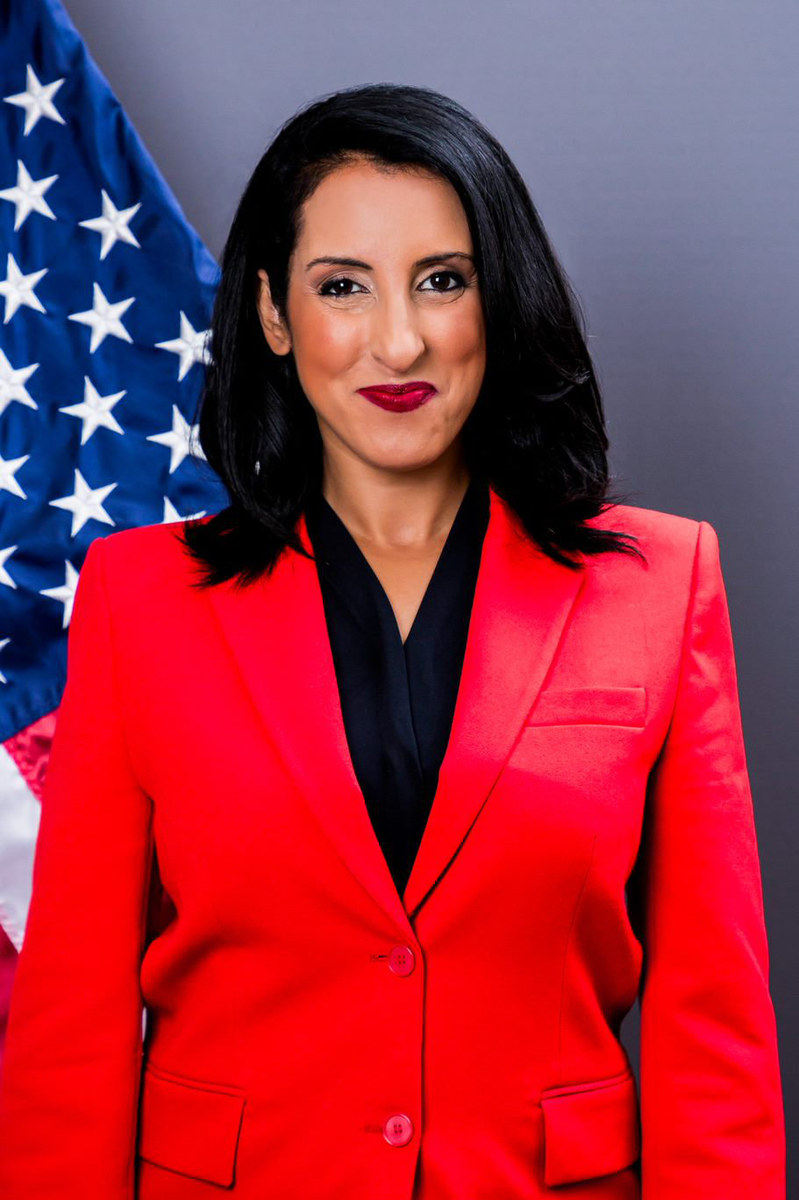

Hala Rharrit, former Arabic-language spokesperson of the US Department of State. (Supplied)
Urging the government to follow those laws, Rharrit said: “We would automatically have to condition our aid and, most specifically, cut our offensive military assistance to Israel.”
By pausing military assistance to Israel, not only “would we ensure, hopefully, that the IDF does not go into Rafah,” but also “regain credibility amongst Arab states as well — that we’re actually conditioning our aid, we’re standing by our laws, we’re standing by international law.
“And that could provide leverage as well, both on the Israeli side and with Arab states to put pressure on Hamas to reach a ceasefire. We have the ability to use our leverage as the US, but we’re not using it at the moment.”
Asked about her resignation, Rharrit said: “I never anticipated resigning, and I certainly never anticipated resigning in protest of any policy.”
But the human tragedy in Gaza “completely changed that,” she told Arab News. “I could not in good conscience remain in government. After 18 years with the State Department, I decided to finally submit my resignation.”
She added: “I spoke up internally. I made my voice and my concerns heard, not based on my personal opinions, but based on what I was monitoring — and I was monitoring pan-Arab traditional and social media.
“And I was seeing and documenting, and reporting back to Washington, all of the growing anti-Americanism… Nothing was convincing anyone, and we had lost credibility.”
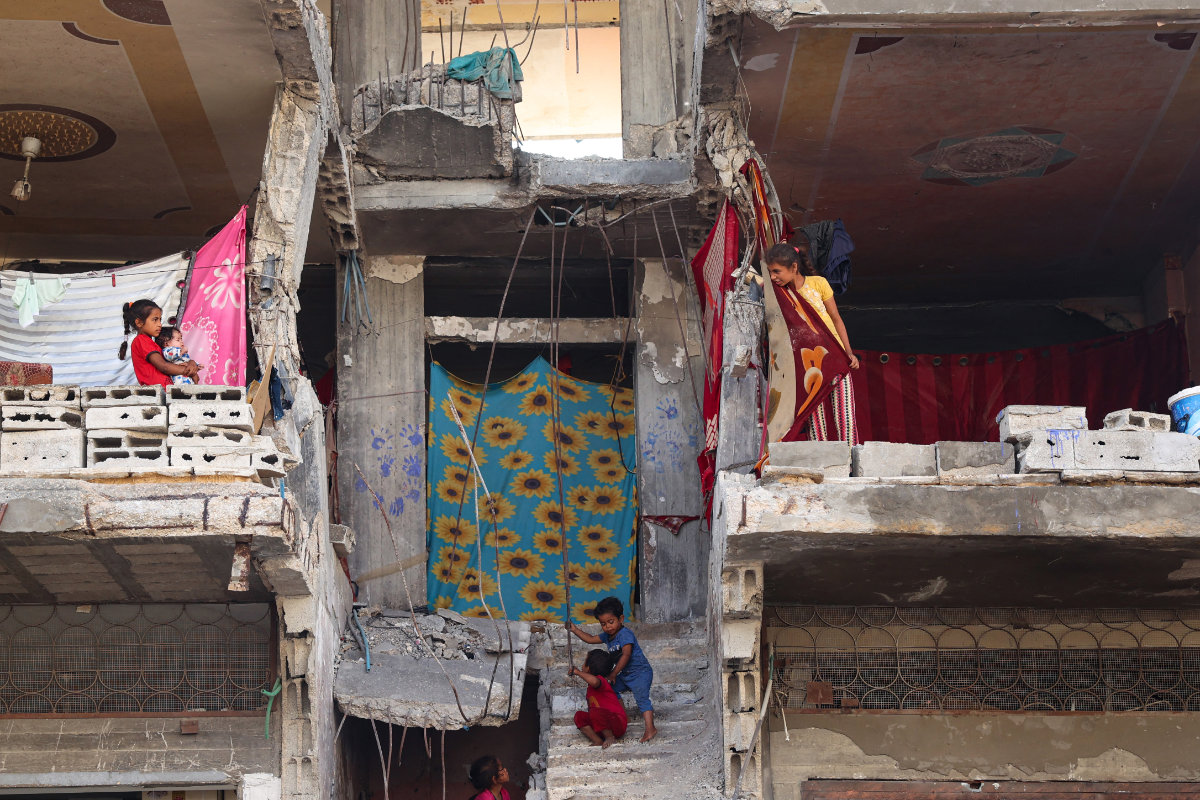

Palestinian children seek refuge at a damaged building in Khan Yunis in the southern Gaza Strip on May 16, 2024, after fleeing their homes amid relentless Israeli bombardment. (AFP)
Rharrit, who previously served as a human-rights officer, continued: “It’s one of the things that we (the US) are known for and that we stand for, but every day I would see human-rights violation after human-rights violation. And it was clear that we had a double standard, and I could no longer support the policy or the administration.”
Despite their expertise, Rharrit said she and her colleagues were not being heard. “Our concerns, our feedback, our documentation of everything that was happening in the region was being ignored — and that was intensely frustrating.”
She said that US policy in Gaza “is a failed militaristic policy that has achieved nothing — over 35,000 Palestinians killed, over 15,000 of whom are children, the hostages remain in Gaza with their families in Israel protesting against Netanyahu and demanding a ceasefire.”
She added: “Despite all this unimaginable suffering and countless attempts by many on the inside to shift policy, it became clear to me that the status quo was resolute.
“Knowing that this policy continued to dehumanize and devastate the Palestinians, generating a vicious cycle of violence, hurting all sides involved, while undermining the US for generations left me no choice but to speak out against the policy from outside government.”
Preceding Rharrit in late March was Annelle Sheline, a foreign affairs officer in the department’s human rights bureau, who left after trying to “raise opposition on the inside,” she told ABC News on April 11.
“Many of my colleagues, people inside the State Department, are devastated by what US policy is enabling Israel to do to Palestinians inside Gaza,” she said.
“They (the Biden administration) continue to send weapons. We’ve seen announcements of new weapons. It’s really shocking that this has been allowed to go on.”
In January, former Biden appointee Tariq Habash, a Palestinian-American, resigned from the Department of Education, saying the US administration “turns a blind eye to the atrocities committed against innocent Palestinian lives.”
In his resignation letter, which he shared on the social media platform X, Habash said his government “has aided the indiscriminate violence against Palestinians in Gaza.”
He added: “Despite claims that Israel’s focus is on Hamas, its military actions simultaneously persist across the West Bank, where there is no Hamas governing presence.”
Since Oct. 7, Israeli troops and Jewish settlers have killed at least 502 Palestinians in the occupied West Bank, according to the Palestinian Health Ministry. Israeli authorities have also arrested more than 7,000 people in the territory, according to prisoners’ affairs groups.
Ten days after Israel began its Gaza offensive, Josh Paul, a former director overseeing US arms transfers, quit the Department of State, citing “a policy disagreement concerning our continued lethal assistance to Israel.”
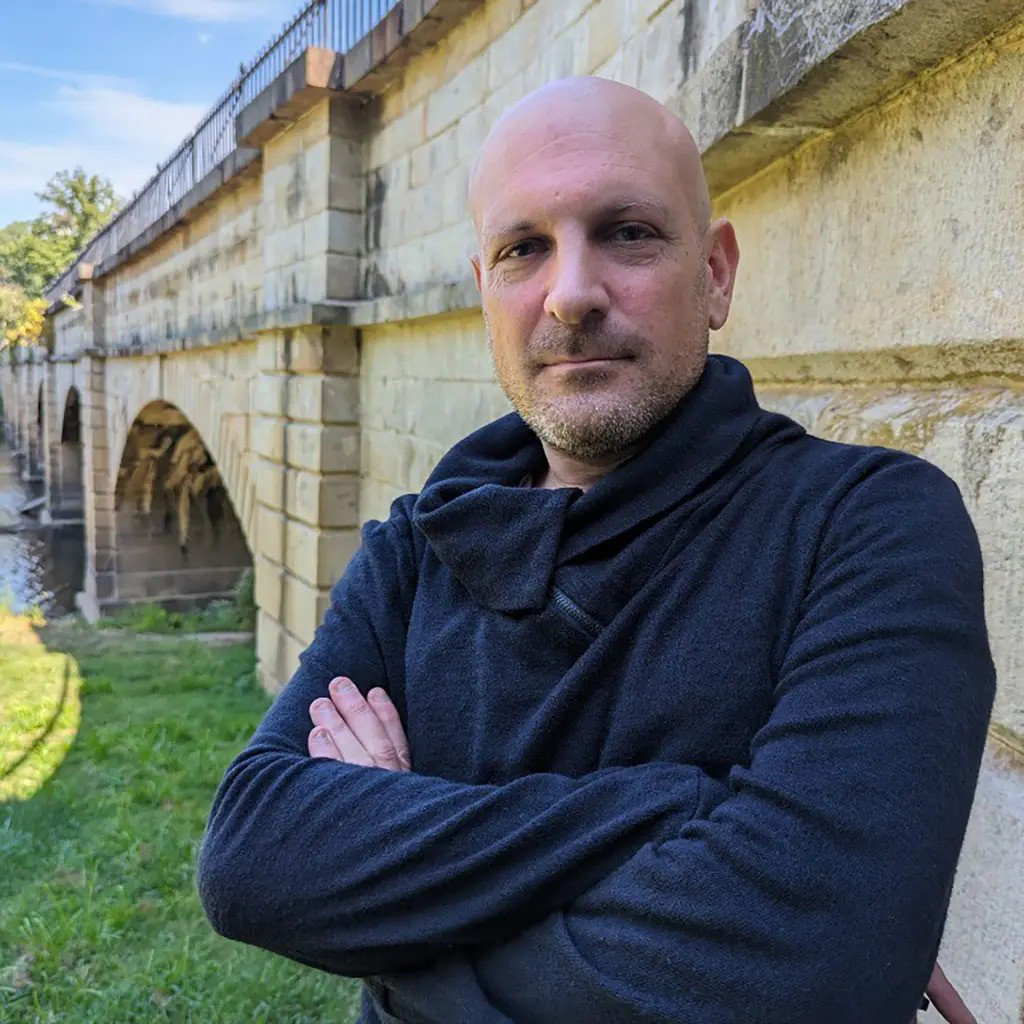

Josh Paul, a former director overseeing US arms transfers, quit the Department of State, citing “a policy disagreement concerning our continued lethal assistance to Israel.” (Supplied)
In a letter he posted on LinkedIn, Paul said his government’s “rushing” to provide arms to Israel was “shortsighted, destructive, unjust, and contradictory to the very values that we publicly espouse.”
He described the Hamas attack on southern Israel as “a monstrosity of monstrosities,” but said he also believed “the response Israel is taking, and with it the American support both for that response and for the status quo of the occupation, will only lead to more and deeper suffering for both the Israeli and the Palestinian people.”
Protests by US administration staffers against its policy in the Middle East have taken various forms besides public resignations. In November, more than 400 of Biden’s employees signed an open letter calling on him to urgently pursue a ceasefire in Gaza.
With the approaching US presidential election complicating Biden’s room for maneuver, the Israeli government committed to continuing its offensive, and with negotiations brokered by Qatar and Egypt making scant headway, such a ceasefire seems unlikely anytime soon.